
Vue.Draggable








Vue component (Vue.js 2.0) or directive (Vue.js 1.0) allowing drag-and-drop and synchronization with view model array.
Based on and offering all features of Sortable.js
Demo
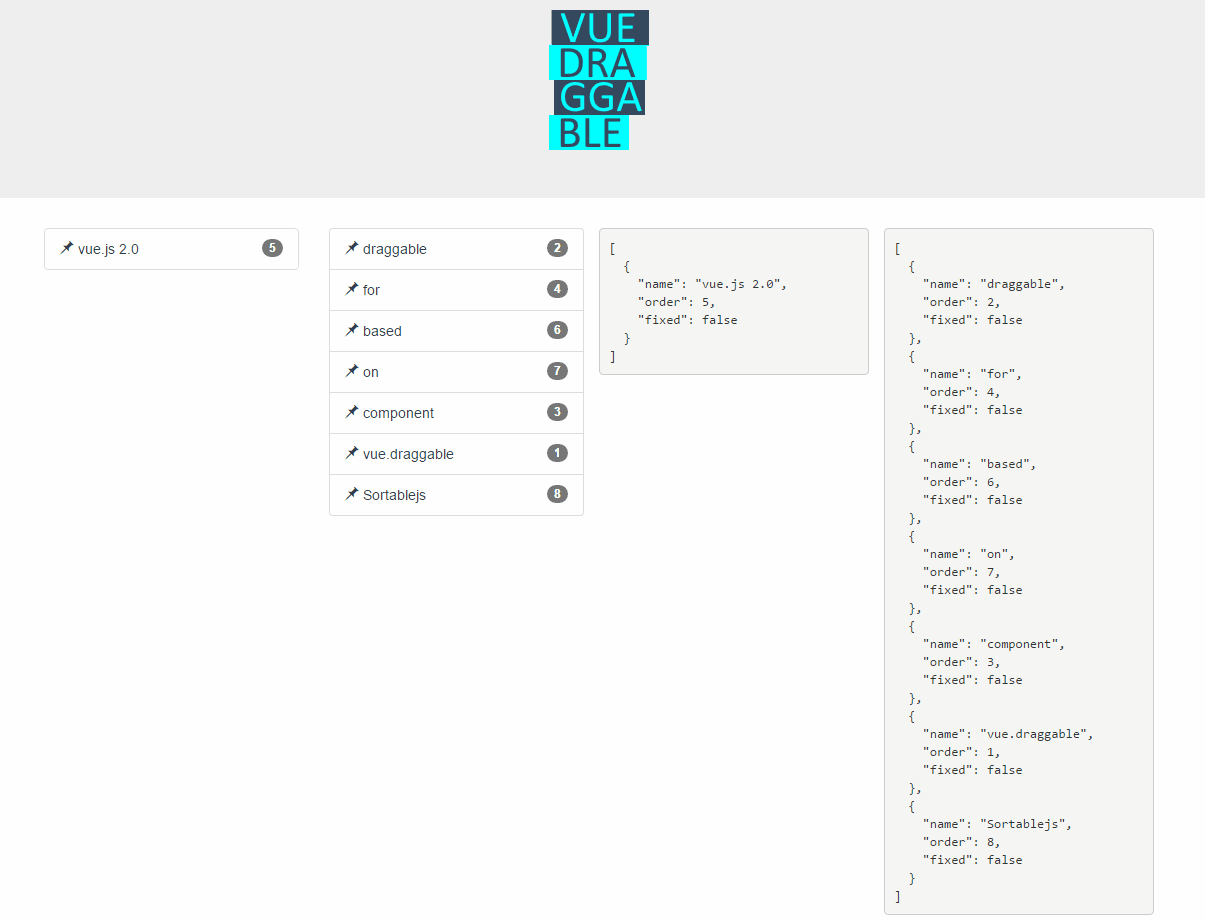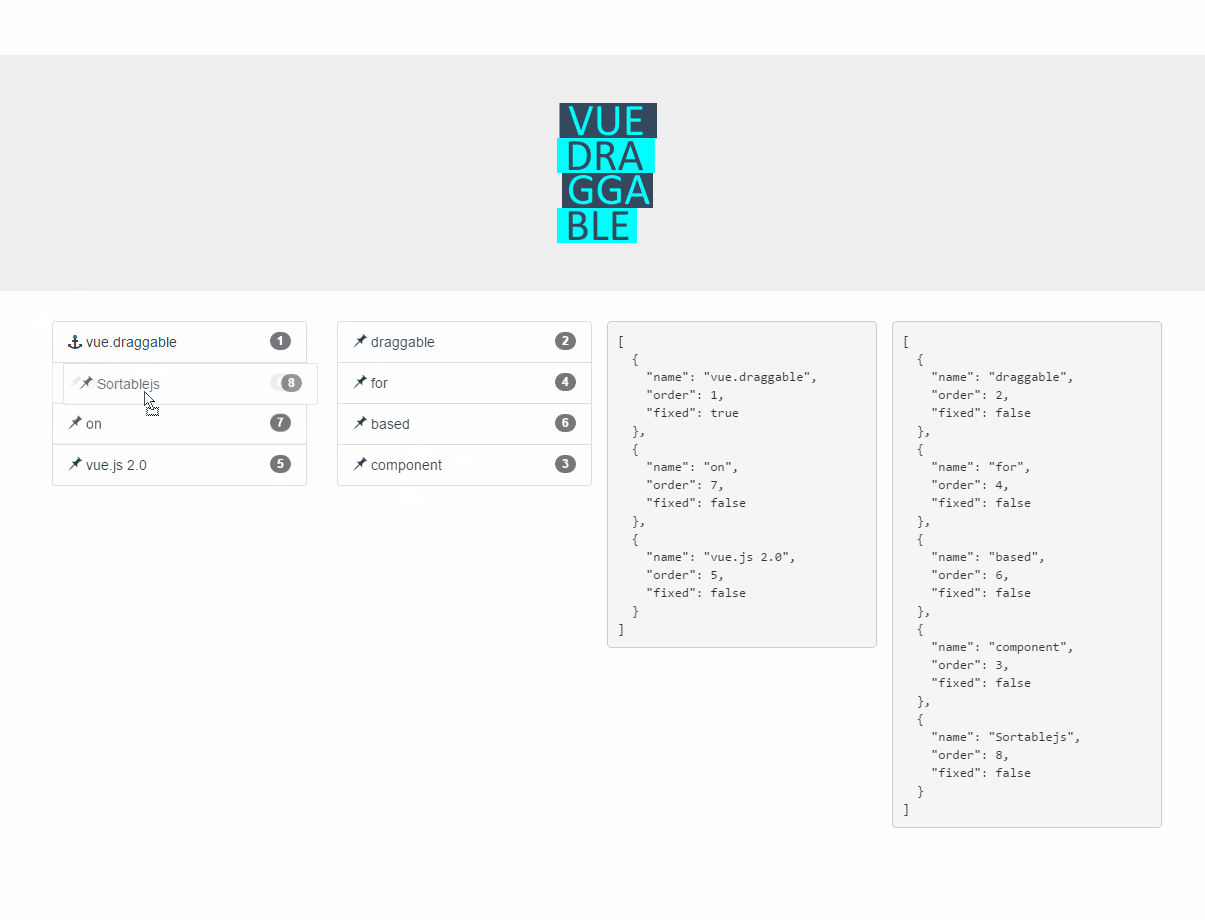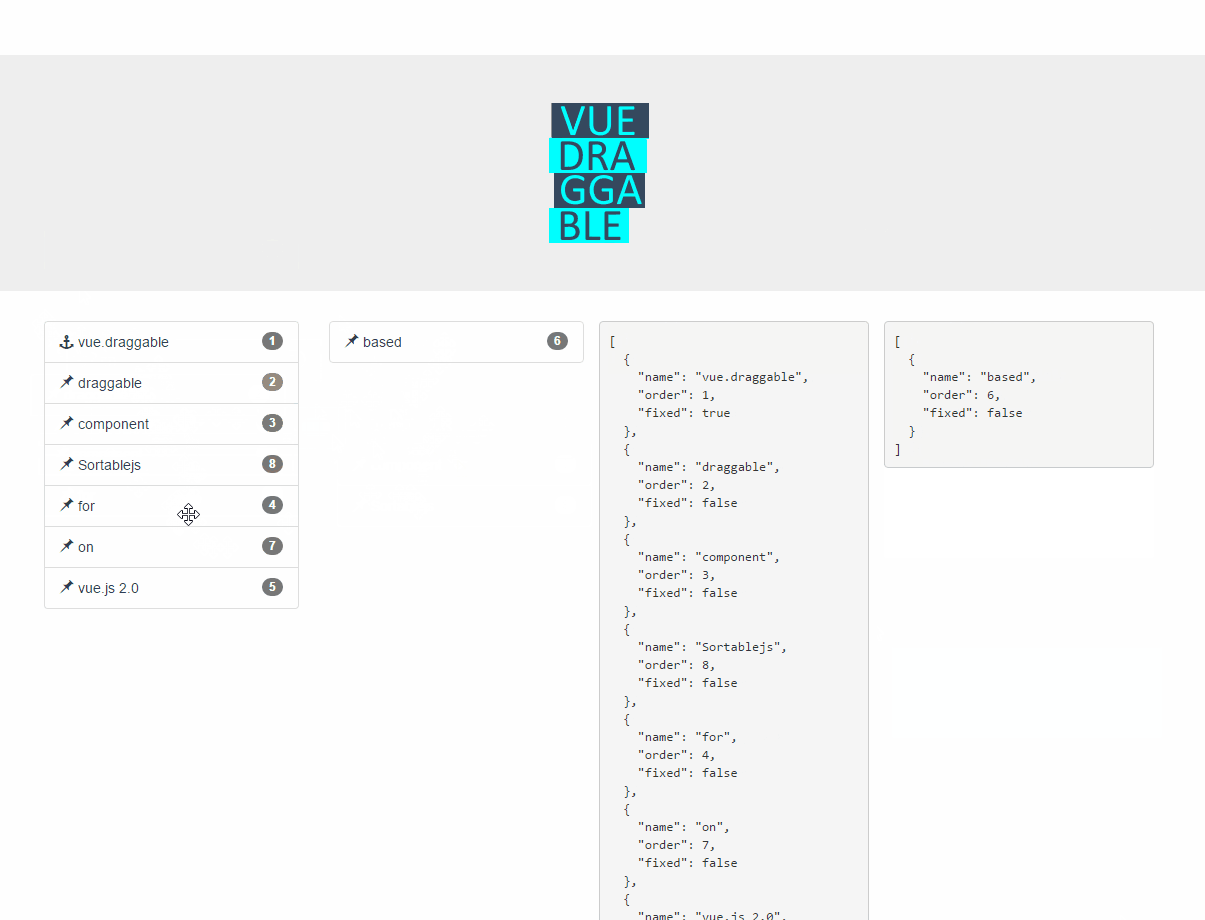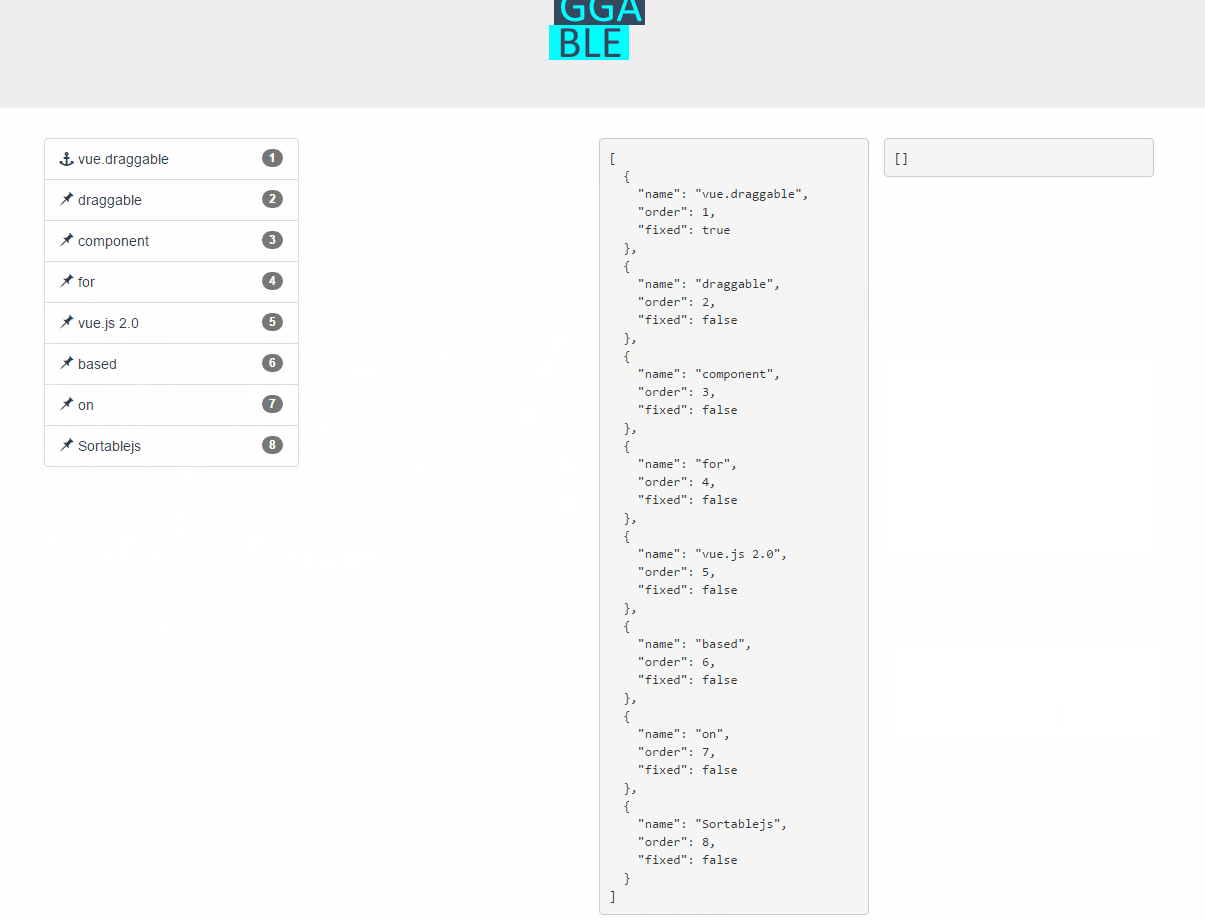
Live Demos
https://sortablejs.github.io/Vue.Draggable/
https://david-desmaisons.github.io/draggable-example/
Features
- Full support of Sortable.js features:
- Supports touch devices
- Supports drag handles and selectable text
- Smart auto-scrolling
- Support drag and drop between different lists
- No jQuery dependency
- Keeps in sync HTML and view model list
- Compatible with Vue.js 2.0 transition-group
- Cancellation support
- Events reporting any changes when full control is needed
- Reuse existing UI library components (such as vuetify, element, or vue material etc...) and make them draggable using
tag and componentData props
Backers

Admin Dashboard Templates made with Vue, React and Angular.
Donate
Find this project useful? You can buy me a :coffee: or a :beer:

Installation
With npm or yarn
yarn add vuedraggable
npm i -S vuedraggable
Beware it is vuedraggable for Vue 2.0 and not vue-draggable which is for version 1.0
with direct link
<script src="//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/vue/2.5.2/vue.min.js"></script>
<!-- CDNJS :: Sortable (https://cdnjs.com/) -->
<script src="//cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/sortablejs@1.8.4/Sortable.min.js"></script>
<!-- CDNJS :: Vue.Draggable (https://cdnjs.com/) -->
<script src="//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/Vue.Draggable/2.20.0/vuedraggable.umd.min.js"></script>
cf example section
For Vue.js 2.0
Use draggable component:
Typical use:
<draggable v-model="myArray" group="people" @start="drag=true" @end="drag=false">
<div v-for="element in myArray" :key="element.id">{{element.name}}</div>
</draggable>
.vue file:
import draggable from 'vuedraggable'
...
export default {
components: {
draggable,
},
...
With transition-group:
<draggable v-model="myArray">
<transition-group>
<div v-for="element in myArray" :key="element.id">
{{element.name}}
</div>
</transition-group>
</draggable>
Draggable component should directly wrap the draggable elements, or a transition-component containing the draggable elements.
With footer slot:
<draggable v-model="myArray" draggable=".item">
<div v-for="element in myArray" :key="element.id" class="item">
{{element.name}}
</div>
<button slot="footer" @click="addPeople">Add</button>
</draggable>
With header slot:
<draggable v-model="myArray" draggable=".item">
<div v-for="element in myArray" :key="element.id" class="item">
{{element.name}}
</div>
<button slot="header" @click="addPeople">Add</button>
</draggable>
With Vuex:
<draggable v-model='myList'>
computed: {
myList: {
get() {
return this.$store.state.myList
},
set(value) {
this.$store.commit('updateList', value)
}
}
}
Props
value
Type: Array
Required: false
Default: null
Input array to draggable component. Typically same array as referenced by inner element v-for directive.
This is the preferred way to use Vue.draggable as it is compatible with Vuex.
It should not be used directly but only though the v-model directive:
<draggable v-model="myArray">
list
Type: Array
Required: false
Default: null
Alternative to the value prop, list is an array to be synchronized with drag-and-drop.
The main difference is that list prop is updated by draggable component using splice method, whereas value is immutable.
Do not use in conjunction with value prop.
All sortable options
New in version 2.19
Sortable options can be set directly as vue.draggable props since version 2.19.
This means that all sortable option are valid sortable props with the notable exception of all the method starting by "on" as draggable component expose the same API via events.
kebab-case propery are supported: for example ghost-class props will be converted to ghostClass sortable option.
Example setting handle, sortable and a group option:
<draggable
v-model="list"
handle=".handle"
:group="{ name: 'people', pull: 'clone', put: false }"
ghost-class="ghost"
:sort="false"
@change="log"
>
<!-- -->
</draggable>
tag
Type: String
Default: 'div'
HTML node type of the element that draggable component create as outer element for the included slot.
It is also possible to pass the name of vue component as element. In this case, draggable attribute will be passed to the create component.
See also componentData if you need to set props or event to the created component.
clone
Type: Function
Required: false
Default: (original) => { return original;}
Function called on the source component to clone element when clone option is true. The unique argument is the viewModel element to be cloned and the returned value is its cloned version.
By default vue.draggable reuses the viewModel element, so you have to use this hook if you want to clone or deep clone it.
move
Type: Function
Required: false
Default: null
If not null this function will be called in a similar way as Sortable onMove callback.
Returning false will cancel the drag operation.
function onMoveCallback(evt, originalEvent){
...
// return false; — for cancel
}
evt object has same property as Sortable onMove event, and 3 additional properties:
draggedContext: context linked to dragged element
index: dragged element indexelement: dragged element underlying view model elementfutureIndex: potential index of the dragged element if the drop operation is accepted
relatedContext: context linked to current drag operation
index: target element indexelement: target element view model elementlist: target listcomponent: target VueComponent
HTML:
<draggable :list="list" :move="checkMove">
javascript:
checkMove: function(evt){
return (evt.draggedContext.element.name!=='apple');
}
See complete example: Cancel.html, cancel.js
componentData
Type: Object
Required: false
Default: null
This props is used to pass additional information to child component declared by tag props.
Value:
props: props to be passed to the child componentattrs: attrs to be passed to the child componenton: events to be subscribe in the child component
Example (using element UI library):
<draggable tag="el-collapse" :list="list" :component-data="getComponentData()">
<el-collapse-item v-for="e in list" :title="e.title" :name="e.name" :key="e.name">
<div>{{e.description}}</div>
</el-collapse-item>
</draggable>
methods: {
handleChange() {
console.log('changed');
},
inputChanged(value) {
this.activeNames = value;
},
getComponentData() {
return {
on: {
change: this.handleChange,
input: this.inputChanged
},
attrs:{
wrap: true
},
props: {
value: this.activeNames
}
};
}
}
Events
-
Support for Sortable events:
start, add, remove, update, end, choose, unchoose, sort, filter, clone
Events are called whenever onStart, onAdd, onRemove, onUpdate, onEnd, onChoose, onUnchoose, onSort, onClone are fired by Sortable.js with the same argument.
See here for reference
Note that SortableJS OnMove callback is mapped with the move prop
HTML:
<draggable :list="list" @end="onEnd">
Slots
Limitation: neither header or footer slot works in conjunction with transition-group.
Header
Use the header slot to add none-draggable element inside the vuedraggable component.
Important: it should be used in conjunction with draggable option to tag draggable element.
Note that header slot will always be added before the default slot regardless its position in the template.
Ex:
<draggable v-model="myArray" draggable=".item">
<div v-for="element in myArray" :key="element.id" class="item">
{{element.name}}
</div>
<button slot="header" @click="addPeople">Add</button>
</draggable>
Footer
Use the footer slot to add none-draggable element inside the vuedraggable component.
Important: it should be used in conjunction with draggable option to tag draggable elements.
Note that footer slot will always be added after the default slot regardless its position in the template.
Ex:
<draggable v-model="myArray" draggable=".item">
<div v-for="element in myArray" :key="element.id" class="item">
{{element.name}}
</div>
<button slot="footer" @click="addPeople">Add</button>
</draggable>
Gotchas
-
Vue.draggable children should always map the list or value prop using a v-for directive
- You may use header and footer slot to by-pass this limitation.
-
Children elements inside v-for should be keyed as any element in Vue.js. Be carefull to provide revelant key values in particular:
- typically providing array index as keys won't work as key should be linked to the items content
- cloned elements should provide updated keys, it is doable using the clone props for example
Example
Full demo example
draggable-example
For Vue.js 1.0
See here













