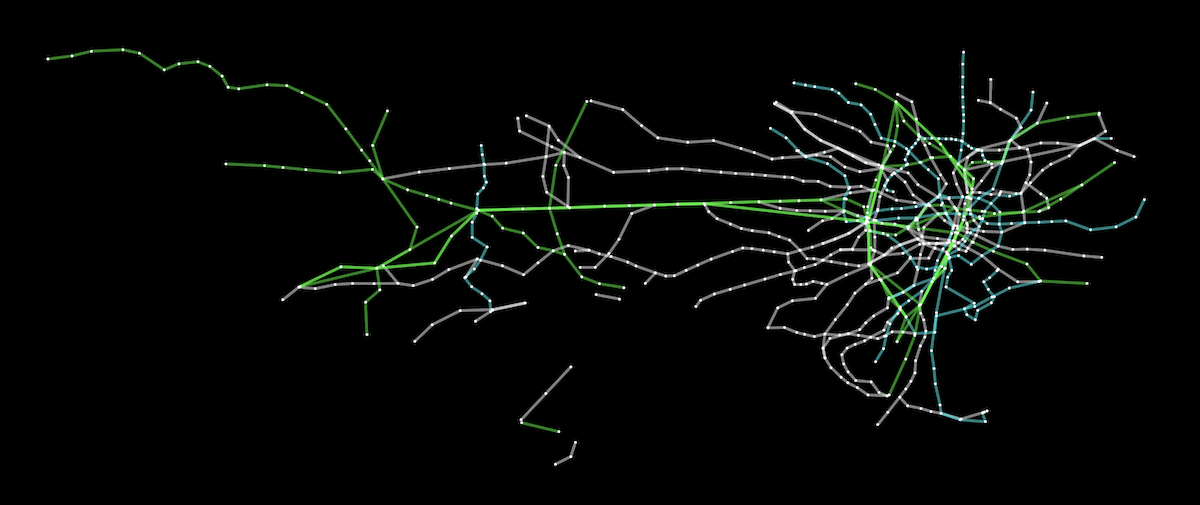
Graph Types
- cytoscape:
cytoscapesupports a wide range of graph types, including directed, undirected, and weighted graphs. It is highly customizable, allowing for the creation of complex network visualizations with various node and edge styles. - vis-network:
vis-networksupports various graph types, including directed, undirected, and weighted graphs. It provides multiple layout algorithms and allows for easy customization of nodes and edges, making it versatile for different types of network visualizations. - d3-graphviz:
d3-graphvizfocuses on directed and undirected graphs, particularly those that can be represented using the DOT language. It excels at creating hierarchical and flowchart-style diagrams, making it ideal for visualizing structured data.
Interactivity
- cytoscape:
cytoscapeoffers extensive interactivity features, including zooming, panning, and selection. It also supports event handling, allowing developers to create interactive visualizations with tooltips, context menus, and dynamic updates. - vis-network:
vis-networkis designed for interactivity, offering built-in support for zooming, panning, dragging, and selection. It also supports events and callbacks, making it easy to create interactive and responsive network visualizations. - d3-graphviz:
d3-graphvizleverages D3.js for interactivity, providing features like zooming, panning, and animated transitions. However, interactivity is more limited compared tocytoscape, and it may require additional coding to implement advanced features.
Layout Algorithms
- cytoscape:
cytoscapeprovides a variety of layout algorithms, including force-directed, circular, grid, and hierarchical layouts. It also supports custom layouts and allows for the integration of third-party layout algorithms, making it highly flexible for different visualization needs. - vis-network:
vis-networkoffers multiple built-in layout algorithms, including hierarchical, force-directed, and circular layouts. It allows for easy switching between layouts and provides customization options, making it user-friendly for various types of network visualizations. - d3-graphviz:
d3-graphvizprimarily uses Graphviz's layout algorithms, such as dot (hierarchical), neato (force-directed), and circo (circular). These algorithms are well-suited for structured and hierarchical data, but the library is less flexible for custom layouts compared tocytoscape.
Integration
- cytoscape:
cytoscapeintegrates well with other data analysis tools and libraries, including Cytoscape.js for web-based applications and Cytoscape desktop for more advanced analysis. It also supports integration with React, Angular, and Vue.js, making it versatile for modern web development. - vis-network:
vis-networkis a standalone library but can be easily integrated with other JavaScript frameworks and libraries. It is designed to be lightweight and modular, making it easy to incorporate into existing projects. - d3-graphviz:
d3-graphvizintegrates seamlessly with D3.js, allowing for the combination of Graphviz's layout capabilities with D3's powerful data visualization features. This makes it ideal for developers who want to leverage both libraries for more complex and interactive visualizations.
Ease of Use: Code Examples
- cytoscape:
Simple graph visualization with
cytoscapeimport cytoscape from 'cytoscape'; const cy = cytoscape({ container: document.getElementById('cy'), elements: [ { data: { id: 'a' } }, { data: { id: 'b' } }, { data: { id: 'ab', source: 'a', target: 'b' } } ], style: [ { selector: 'node', style: { 'background-color': '#666', 'label': 'data(id)' } }, { selector: 'edge', style: { 'width': 3, 'line-color': '#ccc' } } ], layout: { name: 'grid' } }); - vis-network:
Simple graph visualization with
vis-networkimport { Network } from 'vis-network'; const nodes = new vis.DataSet([ { id: 1, label: 'Node 1' }, { id: 2, label: 'Node 2' }, { id: 3, label: 'Node 3' } ]); const edges = new vis.DataSet([ { from: 1, to: 2 }, { from: 2, to: 3 } ]); const container = document.getElementById('network'); const data = { nodes, edges }; const options = {}; const network = new Network(container, data, options); - d3-graphviz:
Simple graph visualization with
d3-graphvizimport { graphviz } from 'd3-graphviz'; const graph = ` digraph G { A -> B; B -> C; C -> A; } `; d3.select('#graph').graphviz().renderDot(graph);