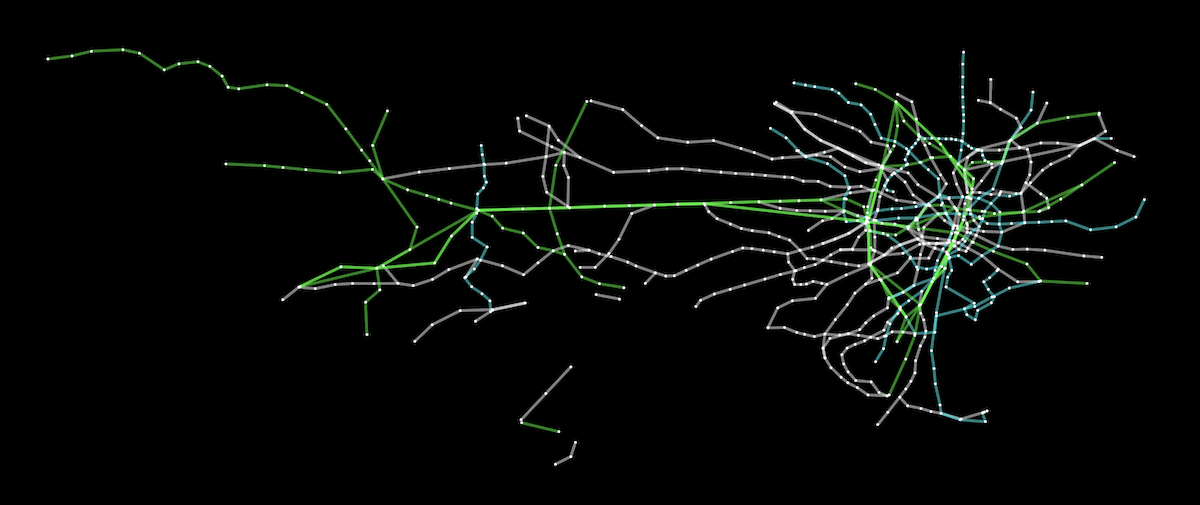
Graph Manipulation
- cytoscape:
cytoscapeprovides extensive graph manipulation capabilities, including adding/removing nodes and edges, updating attributes, and performing complex operations like subgraph extraction and graph cloning. It also supports event handling for user interactions, allowing for dynamic updates and real-time manipulation of the graph. - graphlib:
graphlibfocuses on efficient graph manipulation, providing a simple API for adding and removing nodes and edges, as well as querying graph properties (e.g., neighbors, degree). It also includes algorithms for calculating shortest paths, performing depth-first and breadth-first traversals, and detecting cycles, making it suitable for algorithmic applications. - graphology:
graphologyoffers a comprehensive set of methods for graph manipulation, including adding/removing nodes and edges, updating attributes, and performing structural modifications. It also supports advanced operations like graph merging, splitting, and filtering, as well as a wide range of algorithms for analysis and manipulation, making it highly versatile for both visualization and data processing. - vis-network:
vis-networkprovides basic graph manipulation features, such as adding and removing nodes and edges, updating attributes, and handling user interactions. However, it is primarily focused on visualization, so its manipulation capabilities are more limited compared to dedicated graph libraries. It supports real-time updates and interactions, allowing for dynamic changes during visualization.
Visualization Capabilities
- cytoscape:
cytoscapeexcels in graph visualization, offering highly customizable rendering with support for SVG, Canvas, and WebGL. It provides advanced layout algorithms, styling options (e.g., colors, shapes, labels), and support for animations and transitions. The library also allows for interactive features like zooming, panning, and dragging, making it suitable for complex and large-scale visualizations. - graphlib:
graphlibdoes not provide built-in visualization capabilities, as it is primarily focused on graph data structures and algorithms. However, it can be integrated with other visualization libraries to render graphs based on the data it manages. Its strength lies in its efficient handling of graph data, which can be leveraged by external tools for visualization. - graphology:
graphologyprovides basic visualization capabilities but is not a dedicated visualization library. It focuses on graph data management and analysis, allowing for integration with other visualization tools and frameworks. The library is designed to be modular, enabling developers to use its visualization features alongside other libraries for more advanced rendering and styling. - vis-network:
vis-networkis designed for interactive network visualization, providing an easy-to-use API for rendering graphs with minimal configuration. It supports dynamic layouts, animations, and basic styling, making it suitable for quick and simple visualizations. The library also allows for real-time updates and interactions, such as dragging nodes and zooming, which enhances the user experience.
Performance with Large Graphs
- cytoscape:
cytoscapeis optimized for performance with large graphs, but its efficiency depends on the complexity of the visualization and the number of elements. The library supports WebGL rendering for better performance with large datasets, and developers can implement techniques like lazy loading, clustering, and simplifying graphs to improve performance further. - graphlib:
graphlibis efficient in handling large graphs, particularly for graph manipulation and algorithmic operations. Its data structures are designed for quick access and modification, making it suitable for applications that require frequent updates and calculations on large graphs. However, it does not provide visualization, so performance considerations are primarily related to data processing. - graphology:
graphologyis designed with performance in mind, especially for handling large and complex graphs. Its data structures are optimized for fast manipulation and traversal, and the library supports efficient algorithms for analysis and processing. However, performance may vary depending on the specific operations and algorithms used, so it is important to consider the use case when working with large datasets. - vis-network:
vis-networkperforms well with moderately sized graphs, but performance may degrade with very large datasets due to the limitations of DOM-based rendering. The library provides options for clustering and simplifying graphs to improve performance, but it is not as optimized for large-scale visualizations as some other libraries. For very large networks, additional performance tuning and optimization may be required.
Ease of Use: Code Examples
- cytoscape:
Basic graph manipulation and visualization with
cytoscapeconst cy = cytoscape({ container: document.getElementById('cy'), elements: [ { data: { id: 'a' } }, { data: { id: 'b' } }, { data: { id: 'c' } }, { data: { source: 'a', target: 'b' } }, { data: { source: 'b', target: 'c' } }, ], style: [ { selector: 'node', style: { 'background-color': '#666', 'label': 'data(id)' } }, { selector: 'edge', style: { 'width': 2, 'line-color': '#ccc' } }, ], layout: { name: 'grid' }, }); // Add a new node and edge cy.add([{ data: { id: 'd' } }, { data: { source: 'c', target: 'd' } }]); // Remove a node cy.remove('#a'); // Update node style cy.style().selector('#b').style({ 'background-color': 'red' }).update(); - graphlib:
Graph manipulation with
graphlibconst { Graph } = require('graphlib'); // Create a new directed graph const g = new Graph({ directed: true }); // Add nodes g.setNode('a'); g.setNode('b'); g.setNode('c'); // Add edges g.setEdge('a', 'b'); g.setEdge('b', 'c'); // Get neighbors of a node const neighbors = g.neighbors('b'); console.log('Neighbors of b:', neighbors); // Calculate shortest path const path = g.shortestPath('a', 'c'); console.log('Shortest path from a to c:', path); // Remove a node g.removeNode('c'); // Remove an edge g.removeEdge('a', 'b'); - graphology:
Graph manipulation and visualization with
graphologyimport { Graph } from 'graphology'; import { Sigma } from 'sigma'; // Create a new graph const graph = new Graph(); // Add nodes and edges graph.addNode('a', { label: 'Node A' }); graph.addNode('b', { label: 'Node B' }); graph.addEdge('a', 'b'); // Visualize the graph with Sigma const container = document.getElementById('graph-container'); const sigma = new Sigma(graph, container); // Manipulate the graph graph.addNode('c', { label: 'Node C' }); graph.addEdge('b', 'c'); // Update node attributes graph.updateNode('a', { label: 'Updated Node A' }); // Remove a node graph.dropNode('c'); - vis-network:
Basic network visualization with
vis-networkconst nodes = new vis.DataSet([ { id: 1, label: 'Node 1' }, { id: 2, label: 'Node 2' }, { id: 3, label: 'Node 3' }, ]); const edges = new vis.DataSet([ { from: 1, to: 2 }, { from: 2, to: 3 }, ]); const container = document.getElementById('network'); const data = { nodes, edges }; const options = {}; const network = new vis.Network(container, data, options); // Add a new node nodes.add({ id: 4, label: 'Node 4' }); // Remove a node nodes.remove(2); // Update node label nodes.update({ id: 1, label: 'Updated Node 1' });